Blockchain
The blockchain is undoubtedly what we can call a Buzzword in the world of technologies. All sectors are beginning to focus on concrete use cases, but few actors can boast of having devised revolutionary solutions. For good reason: blockchain technology is still very complex to understand.

What is the Blockchain?
The blockchain is a technology that allows to store and transmit information transparently, securely and without a central control body. It looks like a large database that contains the history of all the exchanges made between its users since its creation. The blockchain can be used in three ways: for the transfer of assets (currency, securities, shares ...), for better traceability of assets and products and to automatically execute contracts ("smart contracts").
Blockchain Durability and robustness :
Blockchain technology is like the internet in that it has a built-in robustness. By storing blocks of information that are identical across its network, the blockchain cannot:
- Be controlled by any single entity.
- Has no single point of failure.
Bitcoin was invented in 2008. Since that time, the Bitcoin blockchain has operated without significant disruption. (To date, any of problems associated with Bitcoin have been due to hacking or mismanagement. In other words, these problems come from bad intention and human error, not flaws in the underlying concepts.) The internet itself has proven to be durable for almost 30 years. It’s a track record
Transparent and Incorruptible :
The greatest advantages in discussion, are the facts that blockchain is both transparent and incorruptible. Blockchain is so much like the internet in the sense that it cannot be controlled by one single entity and that there is no single point of failure. It is a network that lives in a state of consensus, and is a self-auditing ecosystem of a digital value. Thus the problem of manipulation becomes a thing of the past. These groups of transactions are called "blocks". This results in two important properties :
- Data transparency is integrated into the network as a whole. By definition, they are public.
- It cannot be corrupted. Modifying an information unit on the blockchain would require using a huge amount of computing power, which should be greater than the entire network.
Network nodes
The Blockchain is made up of a network of computer "nodes".
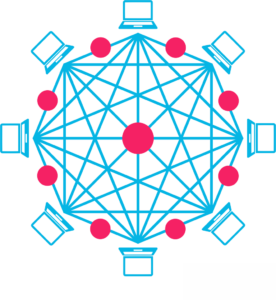
The node (the computer connected to the Blockchain network using a client to validate and relay transactions) obtains a copy of the Blockchain, which is automatically downloaded when connected to the Blockchain network.
Together, the nodes create a powerful second-level network, a totally different view of how the Internet can work.
Each node is an "administrator" of the blockchain and joins the network voluntarily (in this sense, the network is decentralized). However, each of them has an incentive to participate in the network: the possibility of winning bitcoins.
It is said that the nodes "mined" Bitcoin, but the term is somewhat improper. In fact, they are competing to win bitcoins by solving computer puzzles. Bitcoin was the raison of being of the Blockchain as it was originally designed. It is now recognized as the first of many potential applications of technology.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology will probably change the way we live for the next decades. By understanding the concept, we can anticipate the changes it will bring to our lives. In particular, by understanding some of the issues surrounding the adoption of Blockchain technology, we can minimize the impact of Blockchain technology on our own lives.

